Understanding Artificial Intelligence (AI): From Infrastructure to Applications
When people hear about Artificial Intelligence (AI), they often think of futuristic sci-fi scenarios or everyday tools like voice assistants—whether it’s Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, or Google Assistant. While these are great examples of AI applications, the world of AI goes far beyond them.
To understand AI better, let’s break it down into different layers. Think of AI as having a foundation layer (Infrastructure Layer) and an application layer (Application Layer).
Foundation Layer: The Engine of AI
The foundation layer is like the heart and brain of AI, providing the fundamental capabilities that allow AI to function. Imagine you’re watching a show recommended by your smart TV—this recommendation system is powered by machine learning. It analyzes what you’ve watched before and suggests new content based on your preferences and those of similar users.
Another example is Natural Language Processing (NLP), which enables AI to understand human language. When you say, “Hey Google, set an alarm for 8 AM,” the AI processes your request and schedules the alarm accordingly.
This layer includes:
- Hardware (like GPUs, TPUs, and data centers that provide computing power)
- Core AI Algorithms (such as machine learning and deep learning models)
- Cloud Computing (which provides storage and processing power for AI models)
Without this foundation, AI applications wouldn’t work. It’s like trying to watch TV without broadcast signals or cable networks.
Application Layer: Where AI Works for You
The application layer is where AI uses the foundation layer’s capabilities to solve real-world problems. It’s what we interact with directly. Some examples include:
- E-commerce: AI recommends products based on your browsing and purchase history.
- Healthcare: AI assists doctors in diagnosing diseases by analyzing X-rays or MRI scans.
- Transportation: AI optimizes traffic lights to reduce congestion.
If the foundation layer is the “engine” of AI, the application layer is where AI “gets to work” in everyday life.
Going Deeper: Perception, Cognition, and Decision Layers
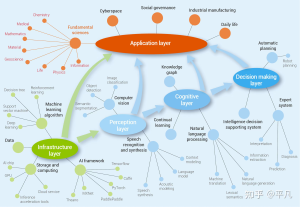
Between the foundation and application layers, AI often includes three additional layers:
- Perception Layer – Gathers information from the world (e.g., speech recognition, image processing).
- Cognition Layer – Processes and interprets data (e.g., NLP, data analytics).
- Decision-Making Layer – Makes decisions based on processed data (e.g., self-driving cars).
Think of this like an electrical system in your house. Power starts from a power plant, goes through transformers to adjust voltage, and finally reaches your home. Similarly, AI must process raw data (Perception), understand it (Cognition), and make decisions (Decision-Making) before delivering useful applications.
The Future of AI and Its Impact
AI’s layered structure shows how different technologies work together to create seamless experiences. Just as society needs well-organized systems for efficiency, AI requires careful coordination across its layers to function effectively.
For those looking to explore AI further, tools like ChatGPT offer a great starting point. They are more accessible and interactive than complex AI models used in industries. Additionally, courses like those offered by online learning platforms can help beginners understand AI in a structured way.
Ultimately, AI is not just a technological advancement—it reflects how we organize, process, and optimize complex systems in our daily lives.
For more insights and updates, visit: dailynewspapers.in